Substation Automation
Looking for Substation Automation Solutions in India? Check Akuntha’s Service for Substation Automation Systems.


Substation Automation
Efficiently control, monitor, and protect your substation equipment with our customer-centric advanced substation automation system (SAS).
Gain real-time visibility and remote operation over your substation operations with our user-friendly interface and intuitive decision-making capabilities.
Rest assured knowing that our SAS strictly adheres to industry standards like IEC 61850, ensuring compatibility, interoperability, and optimised performance for your specific needs.
Experience reliable and efficient substation operation with our solutions that enable fault detection, isolation, and restoration while optimising power flow, voltage, and frequency.
What is Substation Automation System?
Substation automation systems integrate advanced technologies and intelligent systems into electric power substations, utilising components like IEDs, SCADA systems, HMIs, and communication networks. Its purpose is to improve the efficiency, reliability, and safety of power distribution while reducing operational costs. By employing IEDs and SCADA systems, real-time monitoring and control of substations are enabled.
Communication networks facilitate seamless data exchange, and adherence to standards like IEC 61850 promotes interoperability. Substation automation offers benefits such as faster fault detection, optimised power flow, condition-based maintenance, enhanced cybersecurity, and safety. In summary, it optimises substation operation, monitoring, and control to achieve higher efficiency, reliability, and cost savings in power distribution systems.
Components of Substation Automation System
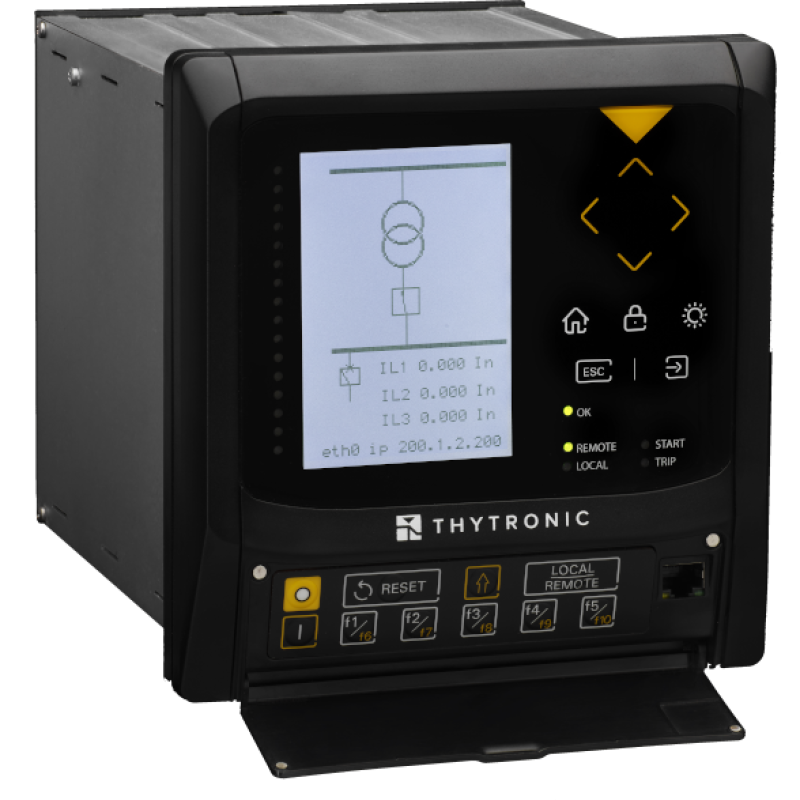
IEDs (Intelligent Electronic Devices)

Intelligent Electronic Devices (IEDs) are critical components of substation automation systems. They play a pivotal role in monitoring, control, and protection functions within electric power substations. These devices, integrated into the substation infrastructure, gather and process data related to electrical parameters, such as voltage, current, and frequency.
They communicate with other IEDs and central control systems, such as SCADA, through communication networks like optical fibre or wireless communication protocols. IEDs support advanced functionalities such as fault detection, event recording, and automation of control actions like circuit breaker operation or load shedding. By adhering to industry standards like IEC 61850, IEDs ensure interoperability and compatibility among different manufacturers’ devices and enable efficient and reliable substation operation.
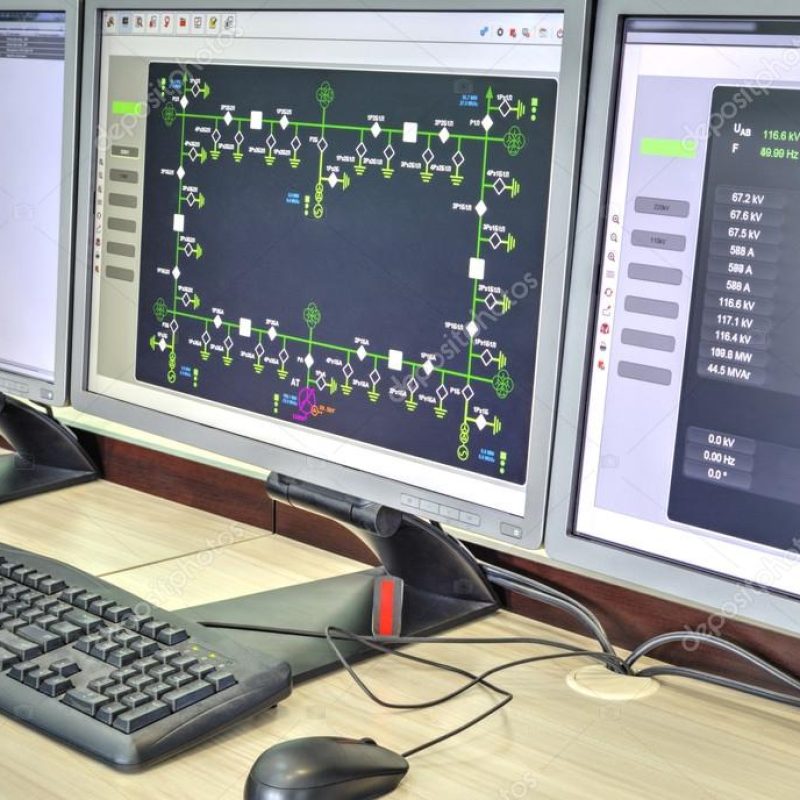


SCADA (Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition)

SCADA, short for Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition, is a key component of substation automation. It serves as a centralised control and monitoring system, integrating intelligent electronic devices (IEDs), communication networks, and human-machine interfaces (HMIs). SCADA enables real-time data acquisition and control of industrial processes, including electric power substations. By collecting and processing data from IEDs through communication networks, SCADA allows operators to monitor and control the substation in real time.
SCADA systems adhere to industry standards such as IEC 61850, ensuring compatibility and interoperability between different devices. They facilitate efficient troubleshooting, analysis of electrical parameters, event reporting, and remote control of substation equipment. Overall, SCADA systems play a vital role in optimizing substation operation, enhancing reliability, and supporting informed decision-making.
HMI (Human Machine Interface)

The Human Machine Interface (HMI) is an essential part of substation automation. It serves as a user-friendly interface that enables communication and interaction between operators and the substation automation system. HMIs display relevant data, alarms, and control options in a graphical format, facilitating easy understanding and operation.
Operators can monitor real-time information, such as voltage levels, power flow, and equipment status, through the HMI. It allows operators to make informed decisions and execute control commands remotely, such as opening and closing circuit breakers or initiating load shedding. HMIs integrate with other substation automation components like SCADA systems, IEDs, and communication networks to provide a comprehensive control and monitoring experience.
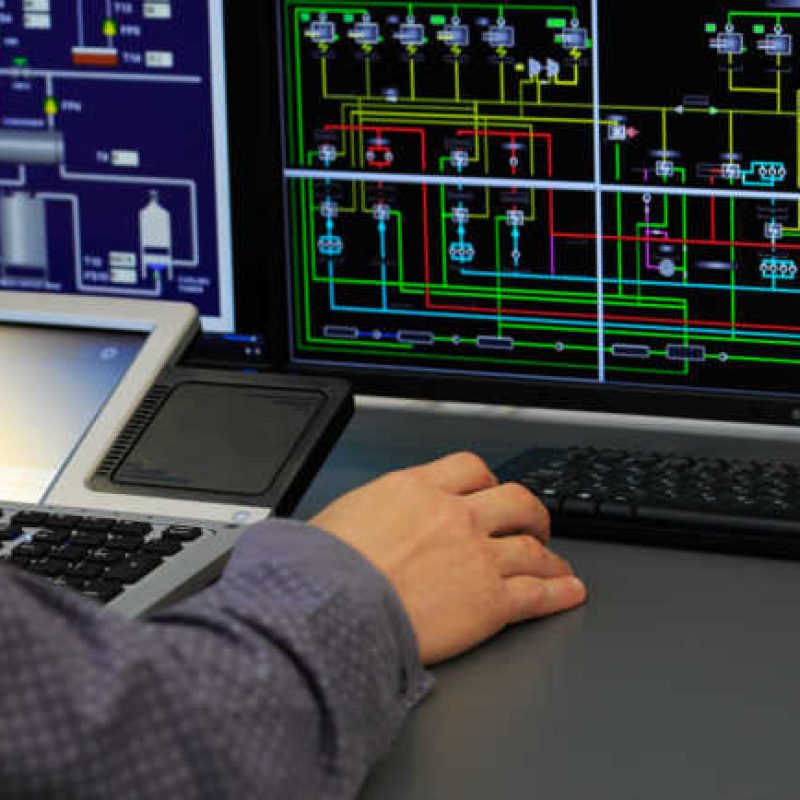


RTUs (Remote Terminal Units)

Substation automation systems require Remote Terminal Units (RTUs), which are crucial parts of the system. They act as intelligent devices that are deployed in distant areas of the substation to make it easier to gather and transmit data to a centralised control system like SCADA. Transformers, switchgear, and other substation equipment, as well as numerous operations, are crucially monitored and controlled in real-time by RTUs.
Through communication networks with wired or wireless protocols, they talk to other parts like IEDs and HMIs. RTUs gather information from sensors, analyse it locally, and then send it to the central control system for evaluation and decision-making. Utilities may increase the efficiency, dependability, and safety of their power distribution networks by incorporating RTUs into substation automation.
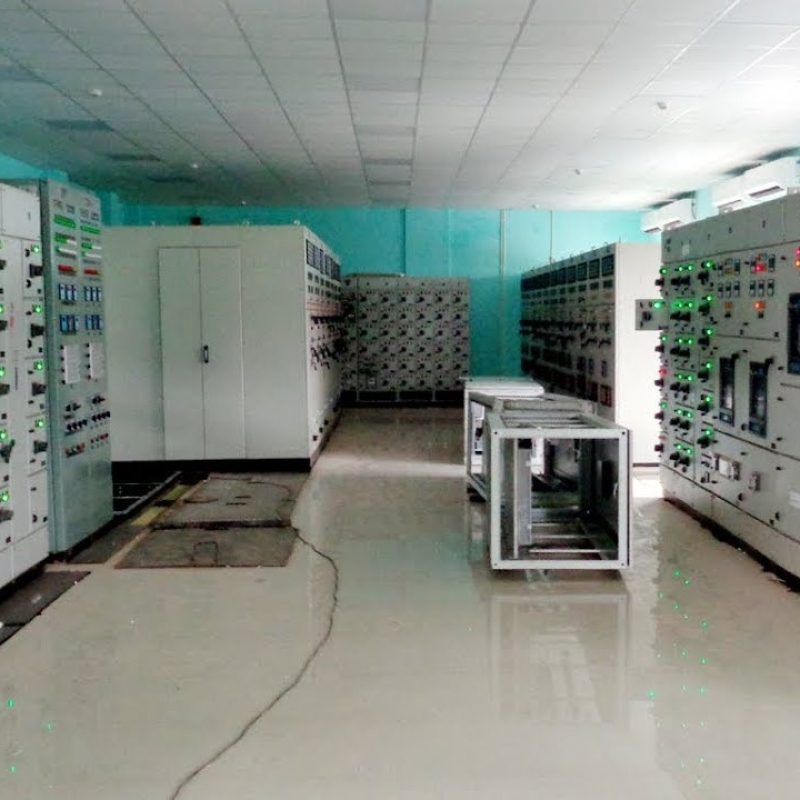
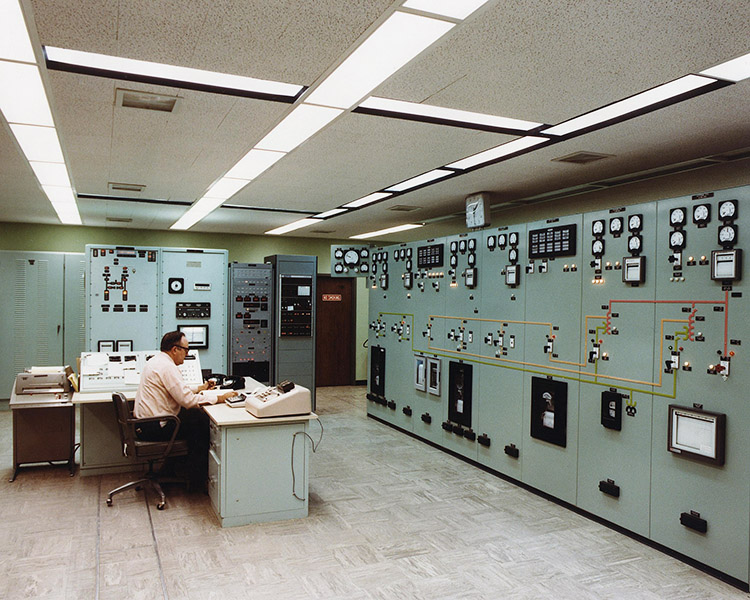
Control Room

Our control room serves as the command center for your substation automation system. Our experienced operators utilize advanced tools and displays to monitor and control your substation in real-time. With a clear visualization of your substation layout and access to data trends, we make informed decisions to optimize your operations.
Our control room enables seamless coordination with field personnel and neighboring substations for efficient response to abnormalities. We priorities cybersecurity measures to protect your control room infrastructure.
Frequently Asked Questions
Substation automation ensures grid reliability by enabling real-time monitoring, faster fault detection, and optimised power flow, enhancing stability. It supports advanced control schemes for efficient fault isolation and restoration. Substation automation also enables predictive maintenance to prevent substation shutdowns.
Substation automation enhances operational efficiency through real-time monitoring, automation of control functions, and advanced data analysis. It streamlines processes, reduces manual tasks, and provides comprehensive insights into substation performance for optimised power flow, proactive maintenance, and efficient resource utilisation.
Communication networks are the backbone of substation automation, enabling seamless data exchange for real-time monitoring, control, and coordination. Wired or wireless protocols ensure reliable and secure data transmission, facilitating efficient communication among substation automation components.
Yes, industry standards like IEC 61850 establish communication protocols and data models for substation automation. These standards promote compatibility among devices from different manufacturers, ensuring seamless integration and efficient operation of substation automation systems.


